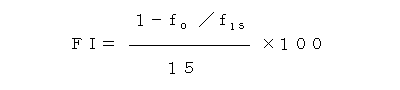Glossary
The technical terms used in this site and the general terms of water treatment are explained on this page. The terms are listed in alphabetic order. Select the term you are looking for from the index on the left.
- Diffuser
- This is an air bubble generator used for efficiently dissolving air in the aeration tank.
- Diffuser type aeration
- This is an aeration method of the activated sludge method in which the compressed air sent from the blower is turned into fine air bubbles, and blown into the mixed solution. When the blown-in air bubbles goes up to the water surface, the solution is mixed, and oxygen is supplied.
- Dissolved oxygen (DO)
- This is molecular oxygen which is dissolved in water, and the concentration is expressed in mg/L.
- Distilled water for injections
- It is one of water standards of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. Normally, it is manufactured by distilling purified water which is acquired by purifying common water by ion exchange treatment, etc. It does not include any bacteria and pyrogens, and it is used for manufacturing injections, water for chemical solution for injection, etc.
- Endotoxins
- High polymers mainly composed of lipopolysaccharide derived from cell walls of Gram-negative bacteria. They usually exist as an aggregate whose molecular mass is 1 million to 2 million. Small part of them exist as a sub unit whose molecular mass is approx. 20 thousand. Therefore, it is not possible to remove them with MF membrane, but it is possible with UF membrane. Most of accidents caused by pyrogens are caused by endotoxins, which cause chills, fever and symptoms of shock only with as small an amount as approx. 5 to 50ng/L of blood concentration. Their are not deactivated by normal sterilization. They has to be decomposed by heat of at least 250 degree C or removed by UF membrane, etc.
- External pressure type
- This is a membrane filtration method which collects filtered fluid in a hollow fiber module or a tubular module by pouring pressurized undiluted solution from outside of them. The activated layer of membrane exist on the outer side of the module which contacts the undiluted solution. Especially the hollow fiber module has features that it is not blocked by suspended substances, and the dirt on the membrane surface can easily be removed by flashing and vibration. On the other hand, its weakness is that the flow of undiluted solution is unbalanced and the performance of membrane is not fully exerted.
- Flashing
- This is a method of washing the membrane surface which washes away the deposits such as the fouling layer, the gel layer, etc. formed on the membrane surface to the undiluted solution discharge side by temporarily and sharply increasing the flow velocity of undiluted solution or water.
- Flat membrane
- Semipermeable membrane formed into plane shape. There are also the types which are integrally formed on woven fabrics or nonwoven fabrics.
- Flock
- The state that fine particles dispersed in liquid loosely become combined and form a coarse aggregate is called floculation (aggregation), and the formed aggregate is called a flock. Flocks have high moisture content and low density, and they disperse by a small stimulus and then gather again changing the form and the particle size.
- Fouling
- A phenomenon that the deposition of poorly soluble components, high-polymer dissolved substances, colloids, minute solids, etc. on membrane decreases the flux. If the deposition occurs inside the membrane, it is called clogging. Fouling advances according to the time of membrane filtration. The degree of recovery from fouling by washing the membrane surface largely varies according to the fouling substances, the membrane and the washing method.
[Products resistant to fouling]
=>Hollow fiber membrane - Membrane module (Large)
=>Hollow fiber membrane - Membrane module (Small / medium)
=>PEARLCOMB diffuser
- Fouling index (FI value)
- This is one of semiquantitative indexes which indicates how much the solution to be filtered causes fouling on the membrane. The test liquid is filtered using the membrane whose pore size is 0.45µm at a pressure of 2.1kg/cm2 for 15 minutes. The initial rate of filtration and the rate of filtration after 15 minutes (f0, f15) are measured, and the FI value calculated according to the formula below is the fouling index.